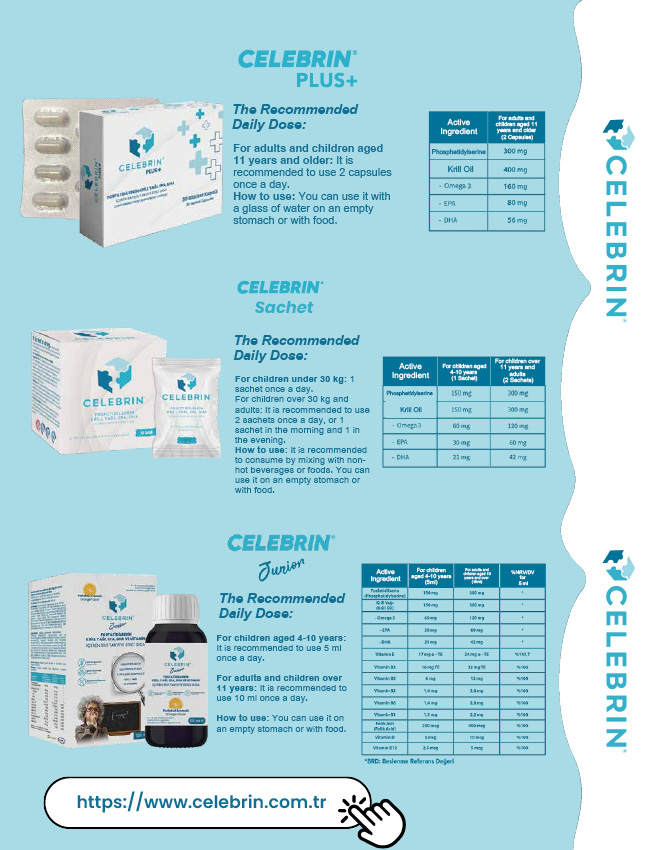
Misconceptions About Breast Milk

There is hardly anyone who becomes a mother and thinks, “I won’t breastfeed my baby.” However, due to misconceptions and false beliefs, many mothers deprive their babies of breast milk. These misguided beliefs not only prevent babies from benefiting from the miraculous properties of breast milk but also deprive mothers of the advantages of breastfeeding. Whether it’s the misconception that “my milk is not enough” or the pressure from the environment, especially from family elders, mothers who turn to formula, often unknowingly deprive their children of the miraculous nutrition found in breast milk. When breastfeeding myths come into play, the situation can become even more complicated.
The benefits of breast milk, which is the most important and often the only food for a baby, are countless. Breast milk strengthens the immune system, preventing various diseases such as asthma, cancer, allergies, and anemia. However, with the widespread use of the internet, some articles can confuse mothers. Today, I want to share with you some misconceptions that I have encountered, especially in the field.
Misconception 1
My milk is insufficient!
In the first few days after birth, a baby’s stomach capacity is only about a teaspoon. Therefore, little milk is produced. It takes up to two days, especially after cesarean deliveries, for milk production to increase. Monitoring the baby is essential to assess breast milk. The mother should be with the baby immediately after birth, and breastfeeding should start within the first hour. In the early days, as long as the baby does not experience excessive weight loss, there is no problem. A weight gain of 25-30 grams per day is expected. If the baby has 6-7 wet diapers and 3-4 soiled diapers per day, and weight gain is sufficient, the baby is getting enough milk. If the diaper count and weight are low, using milk-boosting supplements and breastfeeding support may be necessary.
Misconception 2
My milk isn’t coming; I was raised on formula, and my child will grow up the same way!
Almost every mother who gives birth generally has milk. Concerns about “Will my milk be enough?” after birth decrease milk production. Therefore, mothers should be relaxed. Milk production increases as the mother drinks plenty of fluids and gets enough rest. If the baby is not breastfeeding, breastfeeding education support and milk-boosting supplements can be taken. Breastfeeding should be done as the baby sucks; frequent breastfeeding is necessary. To assess breast milk, evaluation by a pediatrician is essential. If the baby’s weight and urine output are normal, there is no problem with breast milk.
Misconception 3
Eat sweets to increase milk!
Every mother’s physiology is different. Different foods can increase each mother’s milk. The key is for the mother to drink plenty of water and establish a sleep routine. Mothers who drink plenty of fluids and rest will produce more milk. The idea that eating sweets increases milk is wrong. The belief that consuming sweets increases milk is misguided. Increased water intake by those who consume sweets increases milk production. Eating sweets excessively to increase milk has no other benefit than loading the body with sugar. Instead, it will be sufficient to eat a balanced diet, consume milk-boosting foods, and drink plenty of water.
Misconception 4
Your milk is of poor quality, it’s useless!
The quality of milk cannot be determined externally. The milk on the first day and the milk in the first week have different contents. Also, each mother’s milk is unique to herself and her baby. The milk of a baby born on time is different from the milk of a baby born earlier. As long as the child is growing normally, one should not pay attention to different statements about milk. The structure of milk cannot be understood from its color, layer, or density.
Misconception 5
Breast milk is only for satisfying the baby’s hunger!
Breast milk is not only for satisfying hunger but is also crucial for creating a shield against many diseases. Breast milk protects the baby from illnesses; it is the baby’s first vaccine. Breast milk is the ideal source of nutrition containing all kinds of nutrients. It protects the baby from infections and fulfills its water needs. Breast milk plays an important role in jaw and dental development. Children fed with breast milk are more resistant to diseases such as asthma, allergies, and childhood diabetes. It contributes to the baby’s mental, physical, and intellectual development.
Misconception 6
Breastfeeding intervals should be 3 hours apart!
It is generally known to breastfeed every three hours. However, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that babies be breastfed at least 8-12 times a day during the first 6 months when they are exclusively breastfed. Especially in the early days, babies should be breastfed frequently whenever they want. If breastfeeding is tied to a rule, the mother may get stressed, which can lead to a decrease in milk production.
Misconception 7
Breastfeed the baby whenever it cries!
This advice is also incorrect. There are small clues about the baby’s breastfeeding signals. Therefore, breastfeeding when the baby is crying can be challenging because the baby is stressed at that moment and may not want to suckle or may be crying for another reason. The baby should be soothed first, and then the breast should be offered.
Misconception 8
Gas should not be released after every breastfeeding!
Gas should be released after every breastfeeding. The baby can swallow air while sucking, which can cause gas pain.
Misconception 9
Do not breastfeed when you have the flu!
Contrary to this belief, the baby should be breastfed when the mother is sick. The mother should be careful not to have too much respiratory contact with the baby when she is sick. The mother can wear a mask while breastfeeding and wash her hands frequently. The more antibodies in breast milk, the more the baby is protected from illness.
Misconception 10
Breastfeeding prevents pregnancy!
The ovulation cycle continues while the mother breastfeeds. Therefore, contraceptive methods should be used. The timing of menstruation may vary after childbirth. During this period, the mother should consult a gynecologist.
Misconception 11
If you breastfeed constantly, the baby will become dependent on being held!
Especially in the first months, the baby needs trust and touch. In the early days, breastfeeding and holding the baby frequently are necessary. The most calming place for the baby is the mother’s arms.
Misconception 12
Breastfeeding should be stopped after introducing solid food!
Babies are breastfed until the age of one. After the sixth month, complementary feeding begins, and it is called “complementary nutrition.” In the sixth month, 70% breast milk and 30% complementary food are given. When introducing complementary foods, breastfeeding should not be stopped.
Misconception 13
Babies with jaundice should not be given breast milk!
It is absolutely wrong to withhold breast milk from a jaundiced baby. Breast milk should not be stopped; on the contrary, it contributes to the improvement of neonatal jaundice by increasing the baby’s bowel movements. The more the baby breastfeeds, the more beneficial it is.
Misconception 14
Babies should not be awakened to breastfeed!
A misconception is that babies should not be awakened to feed. However, especially in the first months, babies need to be breastfed 8-12 times a day. Although they generally indicate when they are hungry, sometimes they may not wake up from sleep. Therefore, babies need to be awakened and breastfed every 2-3 hours.
Misconception 15
Babies fed with formula are healthier!
There is no scientific evidence that babies fed with formula are healthier. On the contrary, all scientific research indicates that a formula with a perfect content like breast milk has not yet been produced. Breast milk contains immune substances that strengthen the body’s defense system, in addition to nutrients. Breast milk, which is easier to digest, is also free of microbes. Moreover, scientific studies have found that young people who were breastfed in their infancy have higher intelligence levels and perform better in school than those fed with formula.
Misconception 16
Breastfeeding while pregnant poisons breast milk!
The belief that breastfeeding while pregnant poisons breast milk is one of the myths about breastfeeding. If a mother breastfeeds while pregnant, she can continue to breastfeed and nurse her baby during this period. However, it is necessary to supplement the diet with additional food while pregnant. Especially for bone health, calcium supplementation should be done. The mother can continue to breastfeed after giving birth, as long as she receives additional food and can breastfeed both babies together. This is called Tandem breastfeeding.
Misconception 17
The milk waiting in the breast sours!
Sometimes, mothers who cannot breastfeed their baby for various reasons believe that the milk waiting in the breast sours and express and discard their milk. This belief is nothing but a superstition. Breast milk always remains fresh in the breast.
Misconception 18
Breastfeeding for the first 6 months is sufficient!
The baby should benefit from breast milk for at least 6 months. However, this does not mean that breastfeeding should be stopped after 6 months. If the mother still has milk, it is beneficial to breastfeed the baby until the age of 2. Even after introducing complementary foods, priority should be given to breastfeeding, and complementary foods should be given after breastfeeding the baby.