Child Nutrition in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
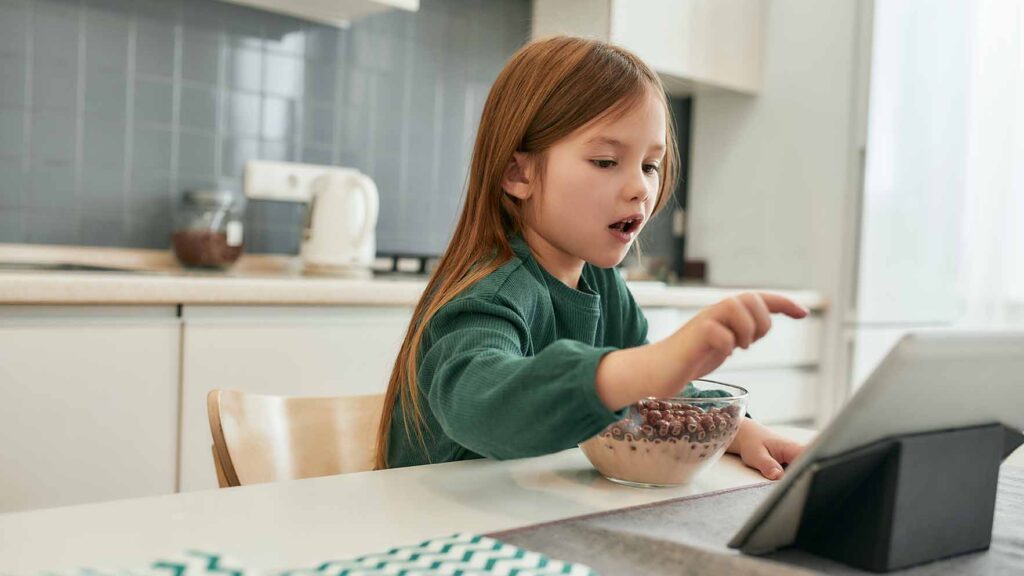

Mobile and interactive screen media occupy a central role in the lives of today’s children. This generation, defined as “digital natives,” is growing up in a digitally enriched world enhanced by mobile media. The age of first interaction with screens has decreased from four years old in the 1970s to just four months today. While electronic devices have brought revolutionary changes in learning, communication, and information sharing, studies have shown the long-term negative effects of screen usage on children’s health. This situation increases the likelihood of facing issues such as obesity, behavioral problems, sleep disorders, and low academic performance.
The Relationship Between Screen Use and Obesity
Epidemiological studies reveal that children who spend more time in front of screens tend to consume fewer fruits and vegetables while increasing their intake of energy-dense snacks, sugary drinks, and fast food. These habits disrupt nutritional balances and increase the risk of obesity. Virtual games and smart devices promote sedentary behavior by negatively affecting levels of physical activity. Intervention programs aimed at reducing screen time have been observed to lead to positive changes in children’s eating habits.
Eating and Screen Interaction
The habit of eating meals in front of screens is one of the significant ways to increase children’s energy intake. Research shows that a large portion of children’s daily caloric intake occurs while they are engaged with screens. This can lead to misinterpretation of satiety cues, reinforcing overeating habits.
Sleep Disturbances and Their Health Effects
Insufficient sleep establishes a connection between screen use, excessive energy intake, and obesity. Studies have found positive relationships between screen time and poor sleep quality. Especially among children aged 3 to 7, sleep deprivation has been associated with obesity. Lack of sleep can lead to imbalances in appetite-regulating hormones, enhancing the tendency to overeat.
Reflections of the Pandemic Period on Digital Health
During the pandemic, digital health applications and remote nutrition counseling became rapidly popularized. As children spent more time at home, they had the opportunity to improve their nutritional habits through such applications. However, this also brought new issues, such as screen addiction.
Artificial Intelligence and Analysis of Anemia and Malnutrition in Children
An examination of childhood anemia in BRICS countries evaluates the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze common nutritional issues among children. AI can facilitate the early diagnosis and treatment of anemia by examining individual nutritional needs and health data. For instance, suitable food alternatives can be suggested for children with specific vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Artificial Intelligence and Nutrition: Future Potential
AI holds significant potential to contribute to the field of child nutrition. This includes creating nutrition plans based on genetic information, assisting parents with smart kitchen devices, and helping children develop healthy eating habits through gamification and educational content. Moreover, AI can provide personalized recommendations by analyzing children’s eating habits.
Children’s food intake can easily be tracked through smartphone applications and wearable devices. This data can be analyzed by nutrition experts to provide tailored recommendations for children’s needs. Parents can also monitor their children’s eating habits through digital platforms and seek assistance from nutrition experts, enabling them to manage their children’s dietary routines more effectively while making the children more conscious of healthy choices.
Changes in Screen Interaction
Recent data shows that children’s interactions with screen media are evolving. Computers, video games, and smartphones are increasing screen time. While there is limited evidence on the effects of these changes on childhood obesity, new media sources have the potential to contribute to weight gain.
Methods for Managing Screen Time
Raising awareness among parents plays a crucial role in reducing children’s screen time. They can monitor screen time using electronic tracking devices and reduce it through various campaigns. Also, activities that promote physical activity and family healthy cooking sessions can help children lead a balanced lifestyle.
Ethical Approaches and Required Regulations
The use of AI in child nutrition must be addressed with careful ethical consideration. Privacy of data, protection of personal information, and accurate information dissemination are of utmost importance. Governments and international organizations should establish strict regulations in this area.
Conclusion: The Potential and Responsible Use of Technology
In conclusion, AI and digital technologies can contribute to developing healthy eating habits in children. However, these technologies must be used effectively and responsibly. Establishing healthy and sustainable eating habits is possible through the proper guidance of digital tools. In the future, it is critical for families and educators to work together to help children lead balanced lives.